99+ Business Cybersecurity Facts and Statistics
Cost of Data Breaches
- Lost business costs contributed a third of the average cost of a data breach (IBM)
- 60% of organizations stated that they had to pass on the cost of a data breach to the consumer by increasing the cost of products and services (IBM)
- Use of artificial intelligence platforms were associated with an decrease in breach costs of $300,075 relative to the average breach – more than any other measure surveyed
- The next most successful measures were:
- Implementing a DevSecOps (development, security and operations): $276,124
- Formation of an incident response team: $252,987
- Extensive use of encryption: $252,088
- The next most successful measures were:
- Globally, the average per record cost of a data breach has reached $164, up 12.3% from 2020 (IBM)
- In Q2 2022, the typical transaction amount requested in a BEC attack averaged $132,559 (APWG Q2)
- The cost-per-incident for a business email compromise attack in the United States increased by a factor of 4 between 2016 to 2021, from $30,000 to $120,000 (US Government Accountability Office)
- In the past five years, there have been 3.26 million complaints to the Federal Bureau of Investigation’s Internet Crime Complaint Center, corresponding to $27.6 billion in losses
- Investment scams were responsible for £3.31 billion of losses in 2022 – more than any other cybercrime (FBI IC3 report)
- The cost of cybercrime damage in 2023 is predicted to be $8 trillion (Cybersecurity Ventures)
- This is larger than the GDP of most countries, including Japan, Germany and the UK, and only smaller than China and the US
- At the current rate of growth, it is expected to cost $10.5 trillion in 2025

- 90% of organizations which have experienced supply chain attacks have suffered financial losses as a result (CrowdStrike)
- The cost of downtime in the wake an attack can be up to 24 times the average ransomware demand for an organization (Datto Ransomware Report 2020)
Industry-Specific Data Breach Facts
- For the 12th year in a row, data breaches in the healthcare sector had the highest average cost of a breach at $10.10 million dollars (IBM)
- Financial ($5.97 million), pharmaceuticals ($5.01 million), technology ($4.97 million) and energy ($4.72 million) completed the top five

- Financial ($5.97 million), pharmaceuticals ($5.01 million), technology ($4.97 million) and energy ($4.72 million) completed the top five
- The financial industry experienced the highest level of targeting among all industries, with phishing attacks accounting for 22-28% of the total attacks in each quarter (Anti-Phishing Working Group)
- Blackberry found that financial institutions were the target of 34% of cyberattacks against their clients (Blackberry 2023 Global Threat Intelligence Report)
- However, the Verizon 2022 Data Breach Insight Report found that the Finance industry had the highest number of successful breaches, the Public Administration, Information and Professional industries were the target of more security incidents by cybercriminals
- The business services sector were the victim of about 13% of ransomware attacks in 2022 (APWG)
- 40% of small business owners are very or somewhat concerned that their organization would be subject to a cyber attack in the next month (CNBC Small Business Playbook)
- Healthcare and public health organizations made up a quarter of the complaints received by the FBI’s Internet Crime Complaint Center from critical infrastructure entities
- Over 60% of all records exposed in data breaches in the United States in 2019 came from the banking and financial services industry (Identity Theft Resource Center)
- Since 2014, hacking/IT security incidents have been the leading cause of data breaches affecting more than 500 records in the healthcare industry, with 44 million medical records compromised in 2022 alone (OCR Data Breach Report)
- Only a third of US citizens believe that social media platforms are capable of protecting their sensitive data from cybersecurity attacks (Reshape)
- However, 71% believe that banks can provide adequate defenses against online threats
Cloud Security
- Cloud migration and remote working were associated with increasing the costs of data breaches (by +$284,292 and +$142,465 relative to the average data breach cost, respectively) (IBM)
- 61% of employees think that files stored in cloud services are always safe from malicious actors and cybercriminals (Proofpoint)

- Three-quarters of those using cloud-native services believe that the number of cloud security tools required for their operations creates “blind spots” and compromises their security operations (PaloAlto State of Cloud Native Security 2023)
- Nearly 40% of organizations reported an increase in the number of breaches following a move to the cloud (PaloAlto State of Cloud Native Security 2023)
- Related to this, 36% experienced increased unplanned downtime following migration to the cloud (PaloAlto)
- 57% of cybersecurity professionals state that cloud security roles are the most difficult to fill (Fortinet 2022)
- A lack of talent in the workforce was identified as the second most pressing challenge in securely moving business operations to cloud services (PaloAlto State of Cloud Native Security 2023)
- Technical complexity was the only issue ranked more highly
- In 2023, 73% of organizations saw a “higher than usual” turnover in their top cloud security roles – stress was cited as a major contributing factor (PaloAlto State of Cloud Native Security 2023)
- Each month, 94% of cloud tenants are the target of a cyberattack (Proofpoint: The Human Factor)
- 31% of companies said that corporate cloud servers were the first point of access for hackers (Hiscox Cyber Readiness Report 2021)
Cybersecurity in the US
- The average cost of a data breach in the US is $9.44 million (IBM)
- This compares to $4.35 million globally
- This is around twice as high as comparable countries such as Canada ($5.64 million), France ($4.34 million), the United Kingdom ($5.05 million) and Germany ($4.85 million)
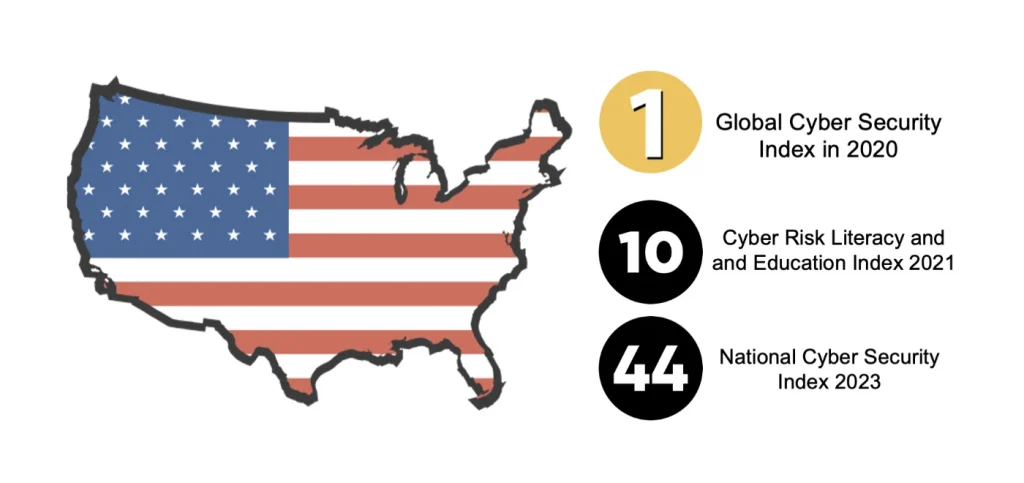
- The United States ranked first in the Global Cyber Security Index in 2020, which measures country’s commitment to cybersecurity though legislation and policies (ITUPublications)
- However, the US ranked on 44th in the National Cyber Security Index 2023, due to especially low scores in protecting digital and essential services (NSCI 2023)
- This placed it between Thailand and Paraguay
- The US ranks 10th on the Cyber Risk Literacy and and Education Index, scoring particularly poorly on government policy. It was ranked between Ireland and Germany (World Economic Forum)
- American companies were the target of 39% percent of ransomware attacks (APWG)
- This is much higher than the next most targeted countries, the UK and France on 5% each
- Just 5% of small businesses believe that cybersecurity poses the biggest threat to their business operations (CNBC Small Business Playbook)
- 38% believe inflation poses a bigger threat
- More than half of American consumers expressed a reluctance to purchase products or services from brands that have fallen victim to cyber attacks (Momentive.ai)
- The 12 largest data breaches in US history are (Techmonitor.ai, Upguard):
- Yahoo! 2013-2016, 3 billion user accounts
- Microsoft Jan 2021 30,000 US companies (60,000 companies worldwide)
- First American Financial Corp May 2019 885 million files
- Facebook April 2021 530 million users
- Facebook/Cambridge Analytica April 2018 50-90 million users
- LinkedIn April 2021 700 million users
- JPMorgan Chase June 2014 76 million households and 7 million small businesses
- Home Depot April 2014 56 million credit cards and 53 million email addresses
- MySpace June 2013 360 million user accounts
- FriendFinder Networks November 2016 412 million user accounts
- Marriott International September 2018 500 million accounts
- Sony’s PlatStation Network 2011 77 million users
- 99% of organizations affected by ransomware in the US had a cyber insurance policy, higher than any other country (Proofpoint State of the Phish)
- In 2022, the Federal Bureau of Investigation’s Internet Crime Complaint Center received over 800,000 complaints about cyber crime and fraud, amount to $10.3 billion in damages and losses
- The FBI’s Internet Crime Complaint Center received 21,832 business email compromise attack complains in 2022, with associated losses of over $2.7 billion
- According to the Center for Strategic and International Studies, some of the most significant cyber attacks against the United States businesses and private sector organizations in the past two years include: (There have been many more attacks on US public bodies and agencies)
- March 2023. US cybersecurity research firms were targeted by a North Korean malware campaign to conduct cyber espionage
- November 2022: Chinese-linked hackers targeted public and private organizations in the United States and other countries since 2021. They employed infected USB drives to distribute malware.
- October 2022. Several US airports were the victim of a Russian DDoS attack, affecting their websites.
- June 2022. Key US industries such as military, software, supply chain, healthcare and pharma were targeted in a massive phishing campaign spoofing Microsoft.
- May 2022. It was revealed that a Chinese hacking group had been stealing intellectual property from US and European companies since 2019.
- April 2022: US companies in the energy, semiconductor and telecom sectors had been targeted by an Iranian-backed phishing cyber espionage campaign
- July 2021: It was revealed that between 2011 and 2018, four Chinese individuals targeted companies, universities, and government entities in the United States to obtain economically valuable information for China’s commercial sectors.
- July 2021. The United States, and other world powers condemned China for the Microsoft Exchange 2021 and the compromise of up to 250,000 servers worldwide. Tens of thousands of US businesses were affected in the attack (NY Times)
- July 2021. The FBI and the U.S. Cybersecurity and Infrastructure Security Agency (CISA) stated that Chinese state-sponsored hackers conducted a spearfishing campaign from 2011 to 2013 targeting US oil and natural gas pipeline companies.
- May 2021, JBS, the biggest meat processing company globally, experienced a ransomware attack that resulted in the temporary closure of its facilities in the United States, Canada, and Australia. REvil, a Russian-affiliated group, was responsible. JBS eventually paid the $11 million ransom to end the attack (BBC News)
- May 2021. The largest fuel pipeline in the United States, the Colonial Pipeline, was hit by a ransomware attack, shutting down the pipeline. A $5 million ransom was paid to the Russian-linked DarkSide group. A lack of multifactor authentication was cited as key reason why the attack was successful (Reuters)
- The US Cybersecurity market generates $68.7 billion in revenue, which surpasses the combined revenue of the next 9 highest countries (Statista Technology Market Outlook 2023)
- The US revenue is expected to grow to £103 billion by 2028
- The US was the target of 46% of all cyberattacks worldwide, for more than any other country (Microsoft Digital Defense Report)
- In 2021, 23% of IT budgets was spent on cybersecurity – an increase of 9 percentage points from 2020, and more than any other country (Hiscox Cyber Readiness Report 2021)
- US companies were joint-most likely country (with Germany) to pay ransom demands, with 21% of victims of successful ransomware attacks saying that they had done so (Hiscox Cyber Readiness Report 2021)
Phishing and Ransomware
- Phishing attacks were 13% more costly than the average breach (IBM)
- Business email compromises were 12% more expensive than average
- Phishing attacks also took longer to identify (219 days) and resolve (76 days) than other breach types (IBM)
- Business email compromise attacks took even longer – 234 days to identify and 74 to contain the breach
- In 2022, the Anti-Phishing Working Group (APWG) recorded 4,744,699 unique phishing sites globally
- The worst quarter was Q3, with 1,270,883 unique phishing sites detected globally(APWG Trends Report Q3 2022)
- August 2022 was the single worst month ever recorded, with a total of 430,141 sites
- Phishing attacks against social media companies comprised 10-15% of all phishing attacks (APWG Q1-4)
- Between January 2019 and December 2022, APWG has seen a 150% increase year-on-year in the number of phishing attacks (APWG Q4)
- Phishing attacks containing malicious URL links are 3-4 times more likely to succeed than those with unsafe attachments (Proofpoint State of the Phish)
- In phishing simulations, nearly 1 in 10 URL-based email “attacks” succeed
- Emails phishing attacks which mention the COVID-19 pandemic are more likely to succeed (17% click rate in phishing simulations; Proofpoint State of the Phish)
- The cost-per-incident of a ransomware attack increased from $1,000 to $13,000 from 2016 to 2021 (US Government Accountability Office)
- However, this was still dwarfed by the costs of BEC and data breaches (nearly £120,000 each)
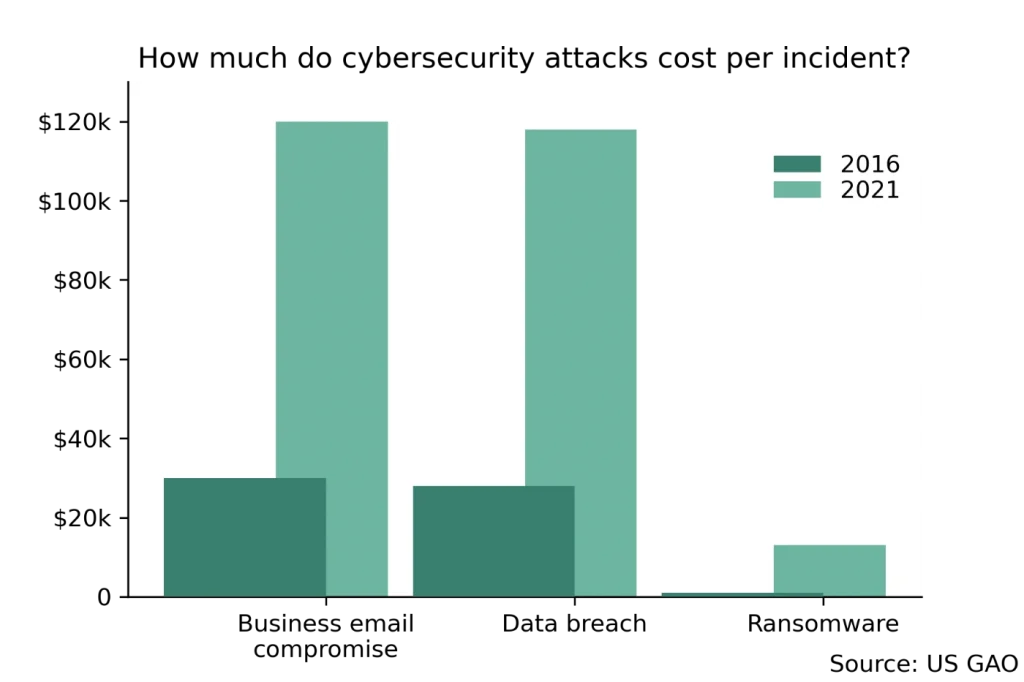
- However, this was still dwarfed by the costs of BEC and data breaches (nearly £120,000 each)
- Only 58% of surveyed employees can define the term phishing (Proofpoint State of the Phish)
- Only 31% could define ransomware
- Phishing attacks were the cause of 40% of the complaints made to the FBI Internet Crime Complaint Center in 2022
- This amounts to 323,972 phishing complaints – up by a factor of 12 since 2018 (only 26,379 phishing complaints)
- 68% of employees believe that their company can automatically block all malicious emails sent to them (Proofpoint State of the Phish 2023)
- In 2021, phishing attacks were the second most common type of cybersecurity attack experienced by organizations in the United States (24% of attacks; Statista/BakerHostetler)
- Ransomware demands increased by in 2021 was $2.2 million, an increase in 144% from 2020 (Unit 42)
- 94% of all cybersecurity attacks launched against organizations use emails and the vector for spreading malware (Verizon)
- This is up from 91% in 2017 (PhishMe)
Cybersecurity Workforce and Training
- 62% of organizations do not believe that their IT security teams are sufficiently staffed (IBM)
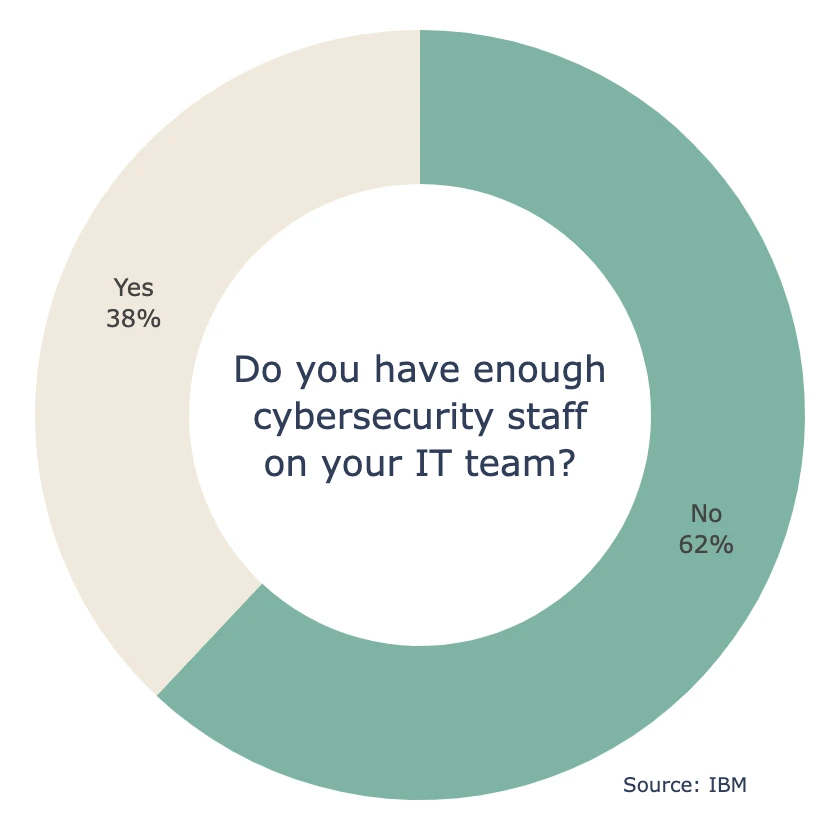
- A lack of cybersecurity expertise lead to an increase in breach costs of $500,000 dollars relative to breaches in organizations with well-staffed teams (IBM)
- Only about 35% of organizations surveyed by Proofpoint ran phishing simulations to train their staff about the dangers of malicious emails (Proofpoint State of the Phish)
- 59% of these organizations ensure that employees who fail phishing simulations receive guidance from the IT security team
- One in three employees do not consider cybersecurity a top priority in their workplace (Proofpoint)
- 43% company employees don’t believe their IT teams are capable of handling cybersecurity incidents (Proofpoint)
- Proofpoint found that 78% of employees use their work devices for personal activities, and 72% use personal devices for work activities
- Around 85% of data breaches were in some way attributed to human error (Verizon DBIR 2021)
- The World Economic Forum found that COVID-19 and remote working was in part responsible for an increase in 125% in the number of cyberattacks from 2020 to 2021
- There were about 163,000 information security analysts working in the United States in 2021 (Bureau of Labor Statistics)
- Information security analysts commanded a high median annual wage in May 2021 was $102,600, higher than other “computer occupations” ($97,430), and much higher than “total occupations” $45,760, highlighting the difficulties in recruiting and retaining talent (Bureau of Labor Statistics)
- Information security analysts are expected to undergo strong demand growth in the decade between 2021 and 2031, with expected increase of 35% (adding 19,500 new openings per year) (Bureau of Labor Statistics)
- The unemployment rate in the cybersecurity industry has been 0% since 2016 (Forbes)
- Chief Information Security Officers and Chief Risk Officers ranked the inability to find employees with appropriate skills as the top challenge in achieving their organization’s cybersecurity targets (Tata Consultancy Services)
- 78% of IT leaders said that it is difficult to hire certified cybersecurity professionals, which is why 91% of them said that their organization is willing to pay for training and certifications for their existing staff (Statista Technology Market Outlook 2023)
- This ranked higher than reliance on legacy IT systems and budget constraints
- “Workforce changes” such as working from home ranked as the second most difficult challenge
- There is a global shortage of 3 million cybersecurity professionals ( International Information System Security Certification Consortium)
- In 2020, nearly two thirds of surveyed cybersecurity professionals considered leaving their current organizations, citing burnout and inadequate compensation (Ponemon Institute)
- One in five organizations with cybersecurity staff shortages said that the inability to hire appropriate staff but them at “extreme risk” of a cybersecurity attack (Statista Technology Market Outlook 2023)
- A further 54% said that they were at moderate risk of an attack
- 88% of organizations believe that they struggle to find adequately skilled individuals or to simply hire enough cybersecurity professionals to staff their teams (Splunk State of Cybersecurity)
- Conducting employee training is associated with a reduction in breach costs of \$247,758 on average (IBM)
Breach and Security Statistics
- In 2022, it took organizations on average 207 days to identify a breach, and a further 70 days to resolve the consequences (IBM)
- Longer breach incidents were associated with an increased cost of 30% relative to shorter breaches
- Only 41% of organizations implement a zero trust security framework (IBM)
- Those that did saw their average breach costs fall to 80% of those who did not implement zero trust security frameworks
- In 2022, 44% of organizations believed that cyber incidents were the biggest risk to business worldwide (Allianz Risk Barometer 2023)
- About two thirds of emails sent in BEC schemes were sent from a Gmail account (APWG)
- Microsoft was the next most common webmail provider exploited, representing about 20% of cases
- 64% of organizations subject to a ransomware attack paid the ransom (Proofpoint State of the Phish)
- 52% of organizations which paid the ransom regained access to their data after the first payment, but 41% had to make additional payments before they could access their data
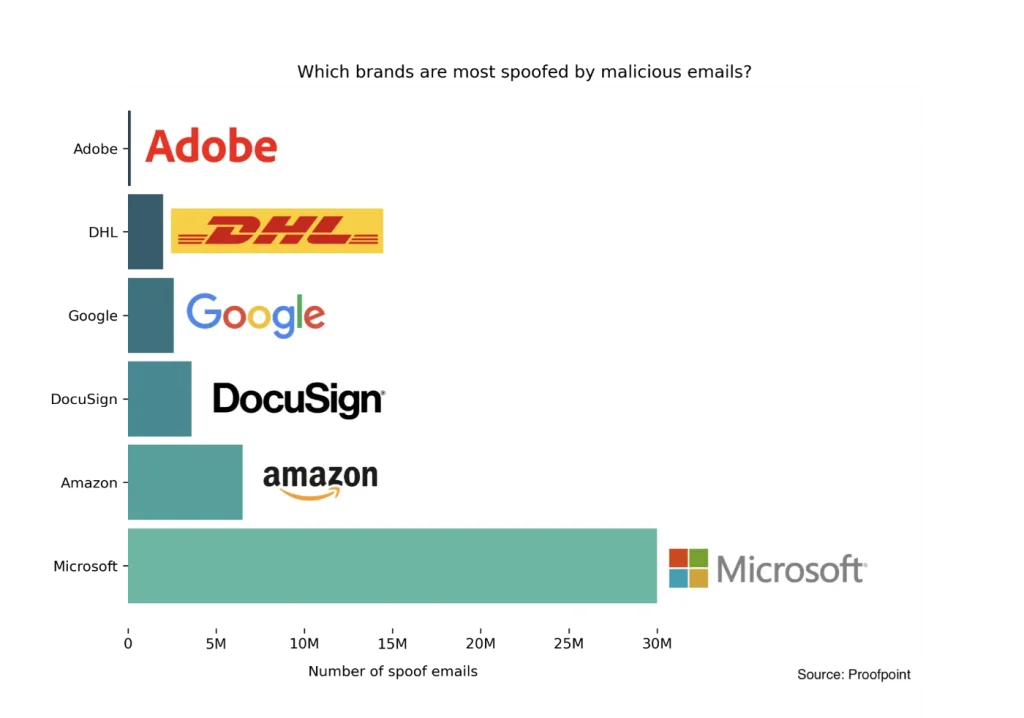
- Microsoft was the most spoofed brand in phishing emails in 2022, with upward of 30 million phishing messages identified using Microsoft branding (Proofpoint State of the Phishing). The next most spoofed brands include:
- Amazon (6.5 million)
- DocuSign (3.6 million)
- Google (2.6 million)
- DHL (2 million)
- Adobe (1.5 million)
- Only 13% of employees said that their work laptop required them to re-enter a password after a period of inactivity, leaving them open to compromise (PC Matic 2022)
- In 5% of private companies, the topic of cybersecurity is rarely, if ever, brought up during board meetings (Tata Consultancy Services)
- Nearly 40% of Chief Information Security Officers and Chief Risk Officers are not confident that their organization could deal with major cybersecurity incidents (Tata Consultancy Services)
- Social engineering attacks were ranked as the the top concern for C-suite cybersecurity professionals (Tata Consultancy Services)
- Attacks using sophisticated techniques such as AI and machine learning ranked as the next greatest concern
- A company falls victim to a cybersecurity attack nearly once every 11 seconds (Cybersecurity Ventures)
- It is estimated that more than 33 billion records will be stolen globally by the end of 2023 (Juniper Research)
- Nearly three-quarters of organizations say that cybersecurity is among their top IT initiatives in the wake of the COVID-19 pandemic (Flexera 2023 State of Tech Spend)
- 46% of organizations said that they are using artificial intelligence, automation and other technologies to help them combat cybersecurity threats (Tata Consultancy Services)
- In 2021, only around 10% of boards had a dedicated committee dedicated to cybersecurity threats (Gartner)
- This is expected to increase to 40% in 2025
- The overwhelming majority of organizations (96%) have said that they are reconsidering and redeveloping their cybersecurity strategies, in part responding to how COVID-19 changed their work practices (PWC Global Digital Trusts Insights 2021)
- In 2021, there was $2.65 billion invested globally in artificial intelligence for cybersecurity and data protection applications (Our World in Data)
- Nearly 7 out of 10 organizations said that they don’t institute a formal approach to cyber resilience in their business practices (Spunk)
- About 80% of all emails sent worldwide in 2020 were spam (Cisco)

Rebecca Murray-Watson
Rebecca Murray-Watson is highly skilled and experienced data analysts. Rebecca has a keen eye for identifying trends, patterns, and anomalies in healthcare data, allowing her to provide valuable insights. Her academic background equips her with advanced statistical knowledge and data visualization skills. Rebecca is adept at distilling complex data concepts into clear and concise insights, making her work accessible and understandable to both technical and non-technical stakeholders. Rebecca’s has a first class science degree from the University of Cambridge and an MSci in natural sciences from University of Cambridge. Rebecca obtained MSc Environmental Modelling from University College London with distinction and is currently completing a PhD from Imperial College London. You can connect with Rebecca via LinkedIn: https://uk.linkedin.com/in/rebecca-murray-watson-0b740995




